Industrial blowers are a type of a blower, which is a system that generates airflow via the force of spinning impellers. Industrial blowers are also frequently referred to as blower fans, fans, and air blowers. Despite this, it’s important to note that, while they’re similar, blowers and fans are not the same thing. Read More…
Since 1991, National Turbine Corporation has been a blower manufacturer, bringing you quality multi stage blowers for use in industrial applications.

#1 Most Reliable Fan Manufacturer. Thousands of customers depend on AirPro fans to keep their operations going, and that's why we build the highest quality fans, prioritize on-time delivery, and offer a 3-year warranty on all products! Founded in 2002, AirPro is privately held and 100% Employee-Owned. With headquarters and manufacturing facilities in Rhinelander, Wisconsin, we offer centrifugal...

Since 1889, The New York Blower Company (nyb) has been a turn-key provider of catalog and custom fans, blowers and ventilation systems. We provide the design, manufacture, installation, maintenance, repair and rebuild of nyb and competitor products. We are constantly expanding, with a worldwide presence of over 200 representatives, and the opening of our fifth manufacturing facility in the US in ...

At DeKalb Blower, we specialize in the design and manufacturing of high-quality blowers that deliver exceptional performance and reliability. Our expertise lies in providing advanced airflow solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of diverse industries. By combining innovative engineering with precision craftsmanship, we create blowers that excel in efficiency, durability, and functionality.

Since 1959, Northern Blower® has offered a wide range of industrial blowers and fans including centrifugal fans, axial fans, swingout fans and custom made fans. Contact us today for information on our quality fans, blowers and equipment. We are committed to the manufacture of a rugged, long-lasting product delivered on time, every time. AMCA Member and ISO 9001:2000 Registered.

More Blower Manufacturers
What are Industrial Blowers & Fans?
Answer: Industrial blowers and fans are robust, heavy-duty machines engineered to move air, gases, or fumes at large volumes and varying pressures, serving as the backbone of countless industrial, commercial, and institutional processes. While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there are important distinctions: industrial fans circulate air at lower pressures primarily for ventilation, cooling, or air movement in open environments, whereas industrial blowers operate at higher pressures, making them essential for applications such as combustion, pneumatic conveying, and air pollution control.
Both utilize rotating blades or impellers powered by electric motors—ranging from compact 1 HP units to massive 1,000+ HP systems—to generate and direct airflow. Air movement is typically measured in CFM (cubic feet per minute), with industrial fans and blowers capable of delivering anywhere from a few hundred to over 100,000 CFM depending on the design and application.
Looking to optimize your industrial facility’s airflow? Explore which blower or fan type is right for your specific process by considering flow rate, pressure, and environmental requirements.
Types of Industrial Fans
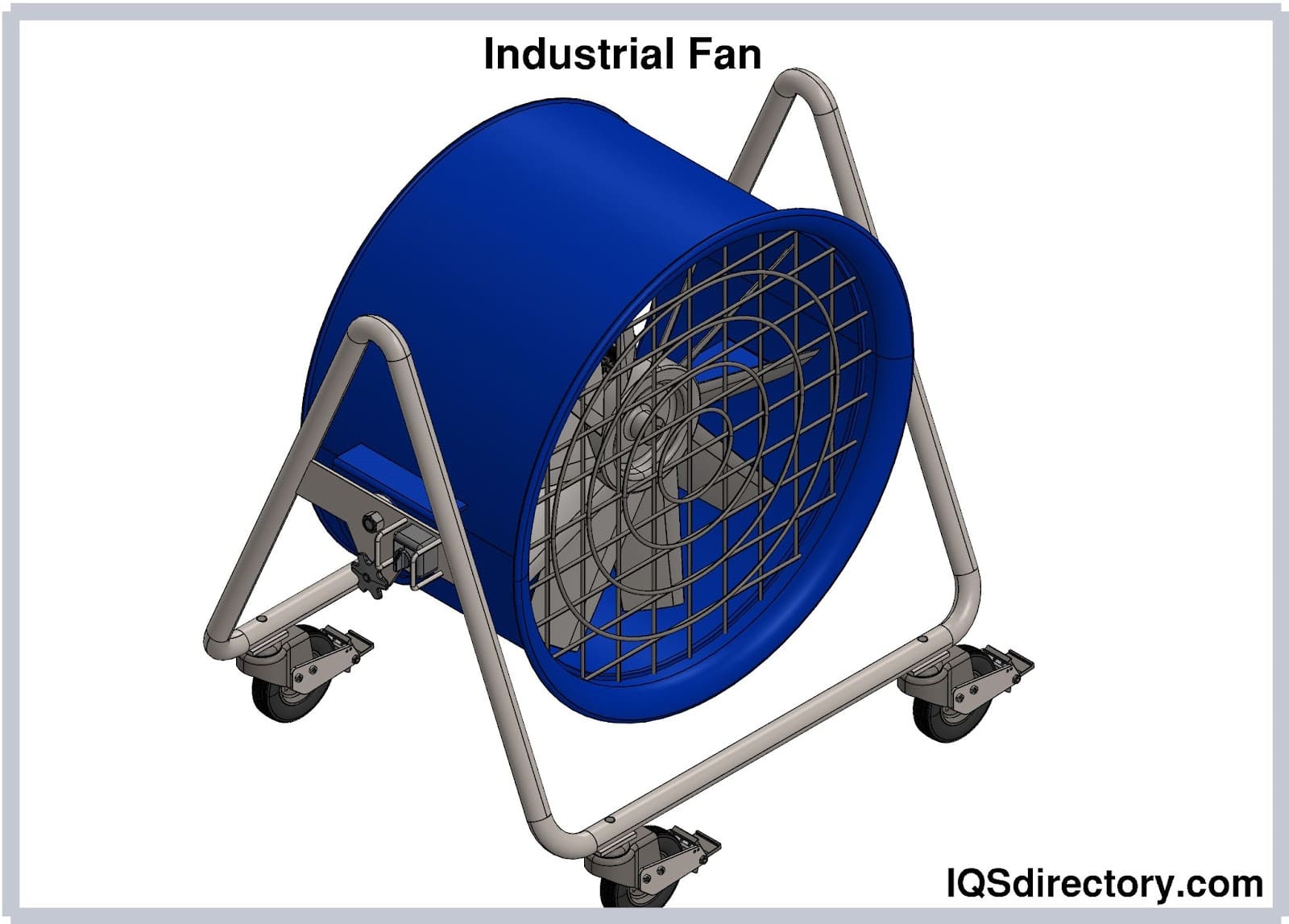
- Axial Fans: Move air straight through the unit, much like a propeller. Ideal for general ventilation, warehouse cooling, and HVAC supply air. Capacity can reach up to 100,000 CFM in large-scale applications.
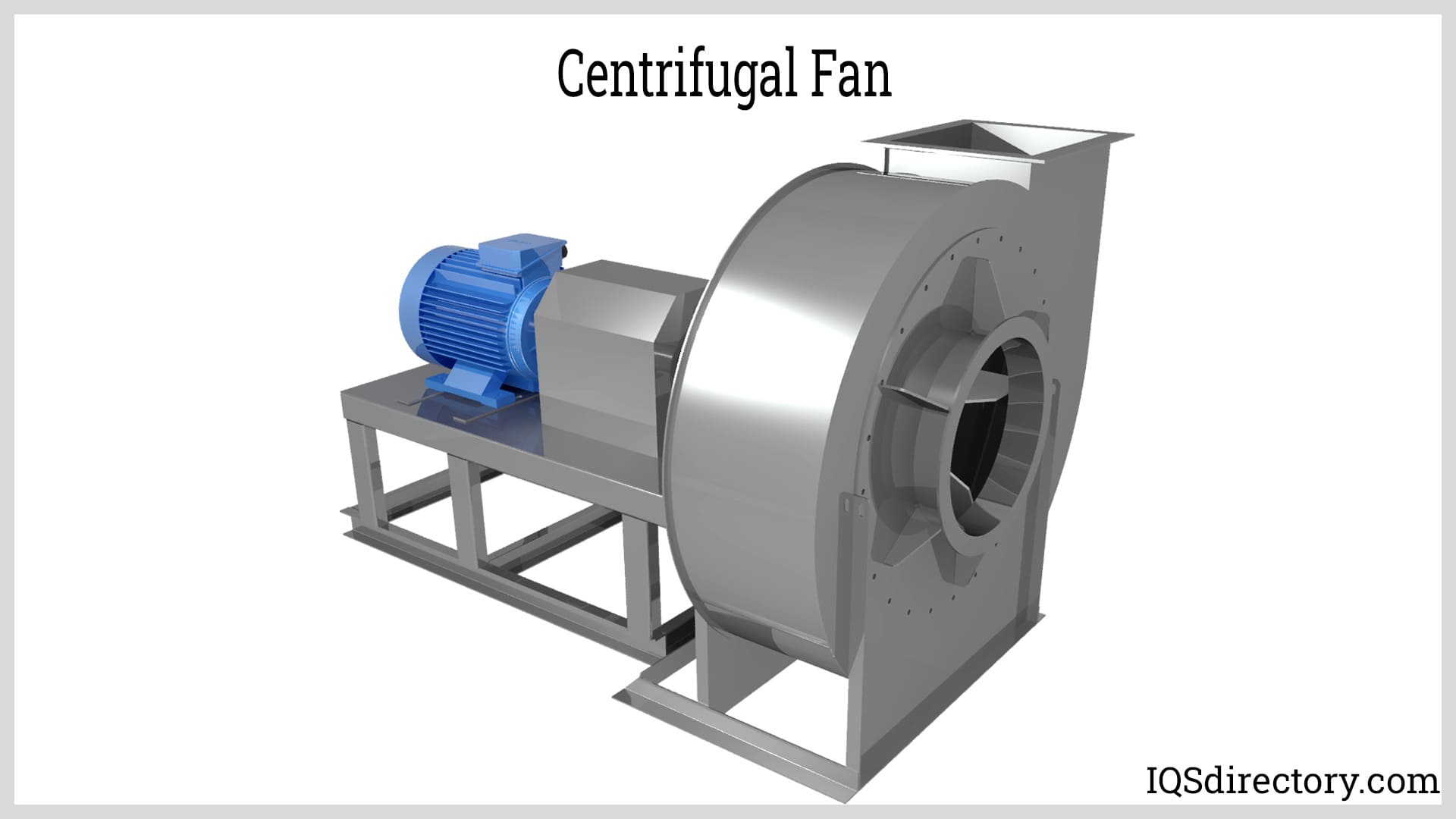
- Centrifugal Fans: Draw air into the center of a rotating impeller and expel it at a right angle. These are excellent for dust collection, fume extraction, and filtration systems, with pressures up to 20 inches water gauge (WG).
Types of Industrial Blowers
- Centrifugal Blowers: Designed for high-pressure scenarios—up to 150 in. WG—these are commonly used in pneumatic conveying, combustion air supply, and heavy-duty dust control.
- Positive Displacement Blowers: Deliver a fixed volume of air regardless of pressure variation, such as the well-known Roots blower. Frequently used for wastewater aeration, pneumatic transport, and vacuum systems.
Constructed from durable materials such as carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, or advanced composites, industrial fans and blowers are built to withstand extreme temperatures (up to 800°F), abrasive dust, and corrosive gases. Applications span manufacturing (drying, cooling, process ventilation), HVAC (air supply and exhaust), power generation (combustion air, flue gas movement), mining (tunnel and shaft ventilation), and more. For instance, a 50 HP centrifugal blower might deliver 10,000 CFM to aerate a wastewater treatment tank, while a large axial fan is vital in clearing smoke or fumes from a busy factory floor.
In summary, industrial blowers and fans are the lungs of modern industry—delivering dependable, high-capacity airflow to keep essential operations safe, efficient, and compliant.
Industrial Blower Applications: Powering Key Processes
Industrial blowers are workhorses designed to move air or process gases at high pressures and flow rates, driving essential operations in nearly every sector. Their versatility and rugged construction make them indispensable wherever continuous, controlled airflow is critical. Below are some of the primary industrial blower applications and real-world examples:
- Pneumatic Conveying
Blowers such as centrifugal or positive displacement models transport bulk materials—grain, cement, plastic pellets—through pipelines. A 20 HP blower, for example, can push 1,000 CFM to transfer flour in a food processing facility. - Wastewater Treatment
Roots-type blowers are crucial for aerating sewage tanks, supplying oxygen (e.g., 5,000 CFM at 10 PSI) to facilitate biological breakdown of waste. Reliable aeration keeps treatment plants operating efficiently and within regulatory limits. - Combustion Air Supply
In power plants, incinerators, or industrial kilns, blowers feed oxygen-rich air to burners. For example, a 100 HP centrifugal blower can deliver 15,000 CFM at 20 in. WG to optimize combustion in a coal-fired boiler, maximizing energy efficiency and lowering emissions. - Dust Collection & Air Pollution Control
Industrial centrifugal blowers are paired with baghouses, scrubbers, or cyclone separators to capture and remove dust, fumes, or particulates from manufacturing and processing environments. A 50 HP blower may handle 8,000 CFM to maintain clean air quality and meet environmental standards. - Drying and Cooling
From drying paint and coatings in automotive plants to cooling extruded plastics or metal components, blowers accelerate production and improve product quality. A 10 HP unit at 2,000 CFM can dramatically reduce drying time and enhance throughput. - Ventilation & Exhaust
Whether clearing toxic gases from chemical plants or providing fresh air in underground mines, industrial blowers ensure safe, breathable environments. Large mine ventilation blowers may deliver 25,000 CFM at 15 in. WG for continuous air exchange. - Vacuum Systems
Blowers generate suction for tasks such as vacuum packaging (e.g., meat or electronics), automated pick-and-place robotics, or industrial cleaning. Systems delivering 500 CFM at 100 in. WG are common in high-speed packaging lines.
Related Use Cases & Emerging Applications:
- Air knife drying on food packaging, batteries, or electronics
- Aquaculture aeration for fish farms and hatcheries
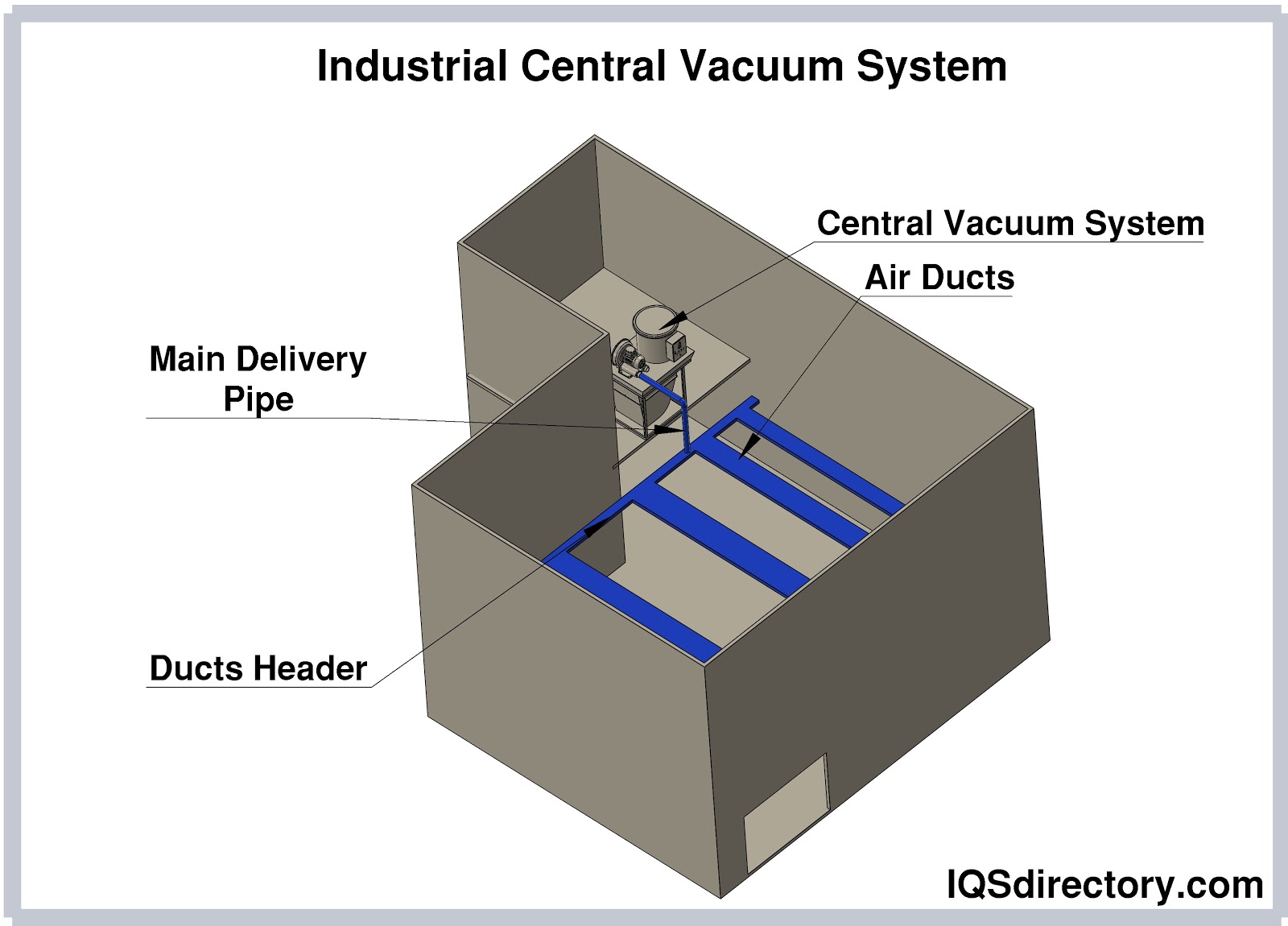
- Central vacuum cleaning in commercial buildings, hospitals, and cleanrooms
- Oxidation and flue gas desulfurization in environmental and energy sectors
- Material handling and separation in recycling and waste management
High-performance industrial blowers—built from steel, advanced alloys, or engineered plastics—routinely handle pressures up to 150 in. WG, temperatures up to 800°F, and aggressive chemicals or particulates. Their reliability, customizability, and safety features make them mission-critical in applications where uptime and compliance are non-negotiable.
Industrial Blowers in Modern Infrastructure: Versatility and Essential Roles
Industrial blowers and fans play a pivotal role in a broad array of environments where precise air movement, temperature, and air quality control are paramount. Applications range from:
- General ventilation in offices, gyms, spas, and commercial buildings
- Industrial cleaning and facility maintenance
- Power generation and energy production
- Disaster relief (smoke removal, emergency ventilation)
- Healthcare and air quality management in hospitals and laboratories
- Cryogenics, food processing, and pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Printing, mining, welding, automotive, pulp and paper, cement, textiles, and packaging industries
Specialty blower types include:
- Side channel blowers – For wastewater, effluent, and sewage treatment, aquaculture, and central vacuum cleaning systems.
- Centrifugal blowers – Utilized in incinerators, HVAC, aeration, conveying, and drying processes.
- Turbo blowers – Used in aeration, combustion air supply, pneumatic bulk transport, air knife drying, and flue gas treatment.
- High-speed centrifugal blowers and air knife systems – Employed in surface drying (e.g., automotive parts, lithium batteries, plastic components, food packaging, and electroplating).
History of Industrial Blowers
The history of industrial blowers is deeply intertwined with the evolution of ventilation technology. One of the earliest records describes a manually operated rotary fan with seven wheels, crafted by Chinese engineer Ding Huan during the Han Dynasty. By the 8th century Tang Dynasty, advancements allowed for hydraulic-powered ventilation systems.
In 16th-century Europe, centrifugal fan blowers ventilated mines—an innovation documented by Georgius Agricola in “De Re Metallica.” Modern breakthroughs followed, with scientists like Robert Boyle and Otto von Guericke exploring airflow and vacuum, laying the groundwork for industrial air movement technology. Architect Sir Christopher Wren incorporated ventilation into the Houses of Parliament, later improved by engineer John Theophilus Desaguliers, who deployed effective fan systems in coal mines and buildings, greatly advancing worker safety.
The industrial revolution ushered in steam-powered fans for hospital ventilation and cooling. The 20th century saw electric-powered blowers become widespread until air conditioning temporarily displaced them, only for blowers to regain prominence due to their superior energy efficiency and lower operational costs.
Recent decades have seen further innovation: In 1998, Walter K. Boyd invented a specialized ceiling fan for dairy barns, minimizing animal stress and dust—technology now common in agriculture and large commercial facilities. Today, the industry offers highly specialized blowers for cleanrooms, laboratories, burn units, and other mission-critical spaces. This ongoing innovation ensures industrial blowers continue to meet evolving demands for ventilation, heating, and cooling.
Types of Industrial Blowers
Industrial blower systems are available in a wide range of designs and configurations, each optimized for specific operational requirements. The most commonly purchased products are exhaust fan systems and general ventilation fan systems.
- Ventilation Fans: Integral to industrial and commercial HVAC systems, ventilation fans circulate and exchange air to prevent buildup of hazardous gases and odors, and to regulate temperature. These are essential for maintaining safe, productive environments in manufacturing, warehouses, and public buildings.
- Exhaust Fans: Designed to remove contaminated air from spaces and expel it via ductwork. Typical in kitchens, bathrooms, laboratories, and manufacturing plants for odor, fume, and particulate removal.
Main Categories of Industrial Blowers
- Centrifugal Blowers (Radial Fans): Used for high-pressure, concentrated airflow. Common in dust collection, industrial vacuum systems, and pneumatic conveying. Subtypes include air foil, backward curve, backward inclined, forward curve, high-pressure, radial blade, paddle wheel, and specialty process gas blowers.
- Axial Blowers: Move large volumes of air at low pressure, ideal for general heating, cooling, or ventilation of large open areas. Subtypes include cooling fans, axial flow fans, tube axial fans, vaneaxial fans, portable blowers, high-temperature axial fans, and variable pitch fans.
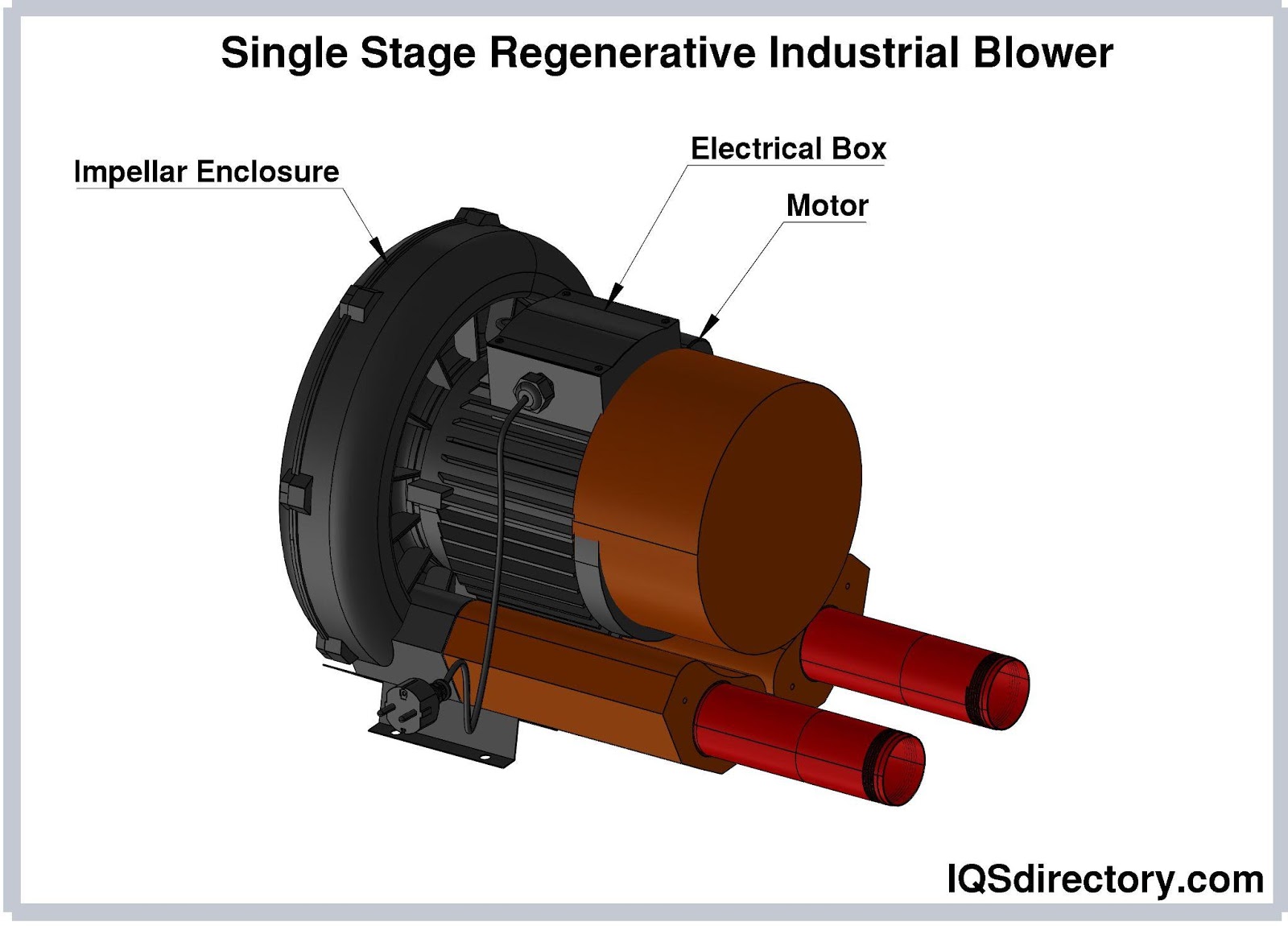
- Regenerative Blowers: Used for aeration in aquaculture, water features, spas, and as vacuum pumps in small-scale or specialty applications. They are also effective in enhancing HVAC airflow.
- Direct Drive and Belt Drive Blowers: Direct drive units offer consistent speed and reduced maintenance, while belt drive systems provide adjustability and are suited for larger, heavier-duty installations where variable speed is required.
- Side Channel Blowers: Designed for pulsation-free vacuum and pressure in wastewater, effluent treatment, and central vacuum systems. Their die-cast aluminum construction ensures durability and silent, maintenance-free operation.
Very large blowers are used for wind tunnels, aerodynamic research, and artificial snow distribution on ski slopes. Portable and specialty fans, such as high-temperature models, serve niche roles in laboratories, cleanrooms, and hazardous environments.
Not sure which industrial blower or fan is right for your project? Contact a blower manufacturer for expert guidance on selecting the optimal configuration based on your application, airflow requirements, and operating environment.
Industrial Blower Equipment Components
Every industrial blower system is engineered with specific components to ensure reliable performance and longevity under demanding conditions. The two primary designs—centrifugal and axial blowers—share some core elements but differ in their airflow mechanisms and construction:
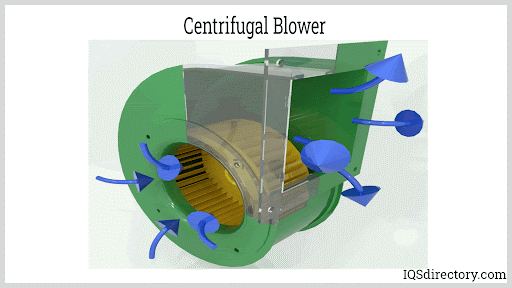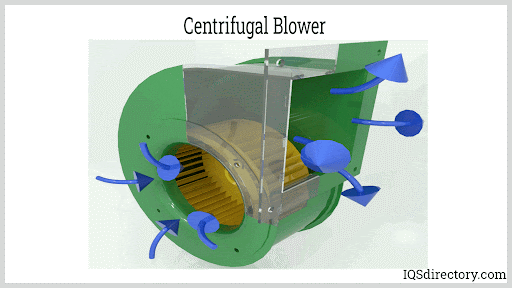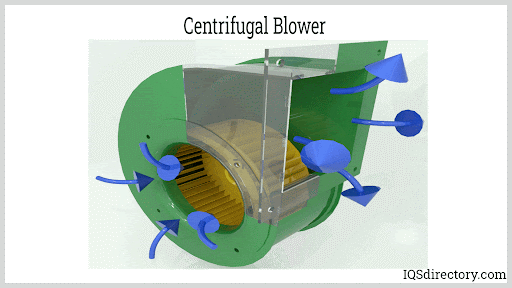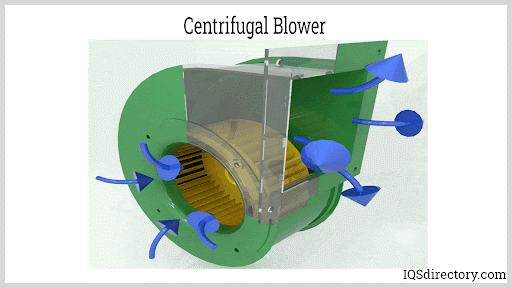
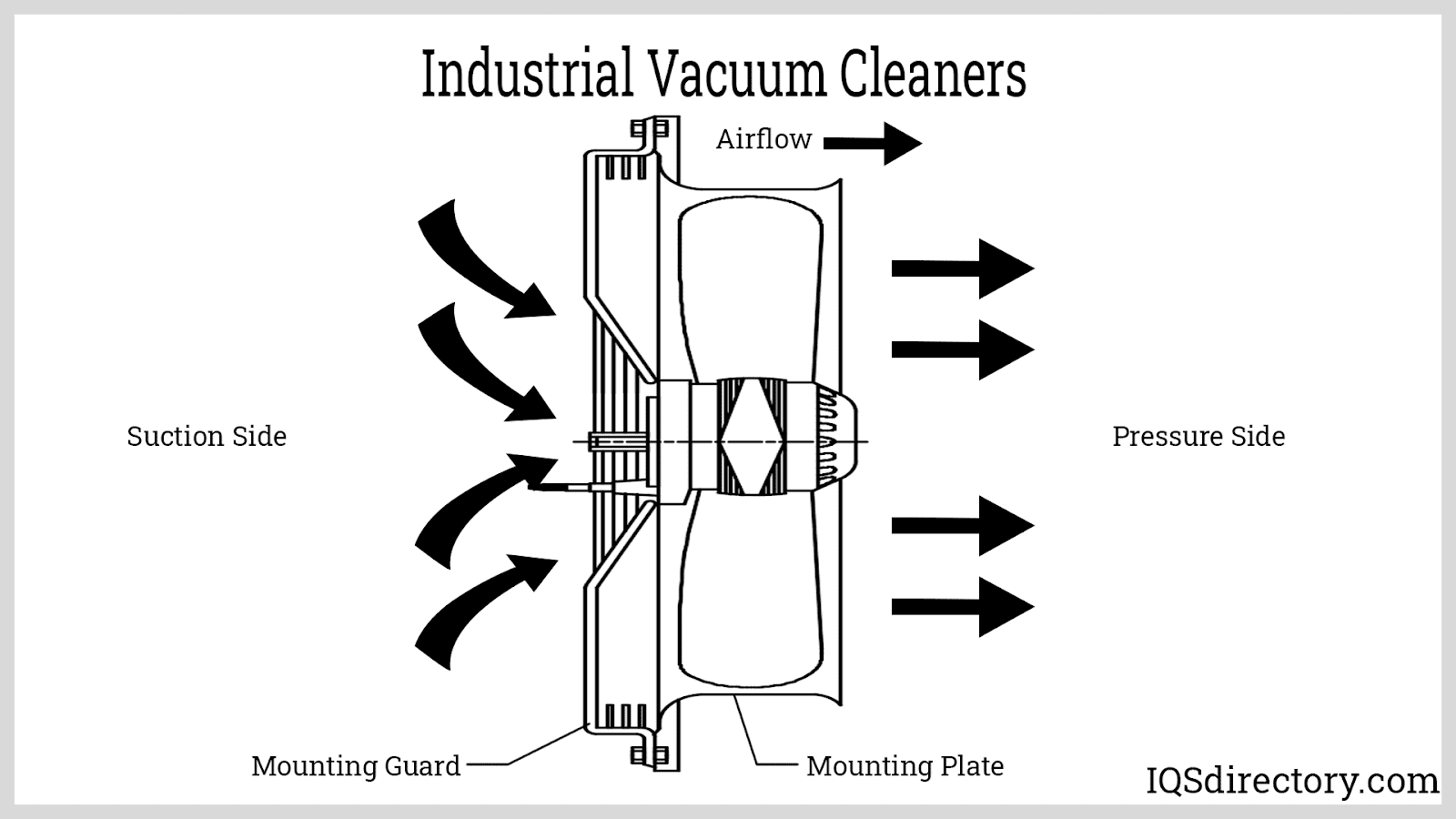
- Centrifugal Blowers: Feature a rotating disk (impeller) with blades and a central hub (collectively known as the fan wheel). As the impeller spins within an annular (ring-shaped) housing, air is drawn in at the center, pressurized by centrifugal force, and expelled at a right angle through an outlet chute. Some designs integrate advanced aerodynamic components to boost efficiency and reduce noise.
- Axial Blowers: Comprise a rotating disk, curved blades, and a central hub. The blades rotate around the axis of the shaft, moving air parallel to the axis in a continuous stream—much like a propeller. This design excels at moving large volumes of air at low pressure for general ventilation and cooling.
Additional components can include variable frequency drives (VFDs) for speed control, acoustic enclosures or silencers for noise reduction, corrosion-resistant coatings, and special bearings rated for high temperatures or aggressive environments.
Benefits of Industrial Blowers
Investing in industrial blowers provides significant operational, financial, and environmental advantages:
- Efficient Air Circulation: Delivers continuous, controlled airflow in large or enclosed spaces, supporting ventilation, process control, and temperature management.
- Energy Savings: Industrial blowers are far more energy-efficient than air conditioning systems for many applications, reducing utility costs and environmental impact.
- Versatility: Available in a wide variety of sizes, configurations, and materials to meet the needs of virtually any industry, from food processing to chemical manufacturing.
- Durability and Reliability: Built to withstand harsh environments, high temperatures, and continuous-duty cycles, minimizing downtime and maintenance.
- Improved Air Quality: Essential for removing dust, particulates, fumes, and gases—helping facilities comply with OSHA, EPA, and other environmental and workplace safety standards.
- Customization: Easily tailored to unique process requirements, including airflow, pressure, material compatibility, and control options.
Looking to increase productivity and workplace safety? Discover how industrial blowers can improve your facility’s efficiency while reducing long-term operating costs.
Industrial Blower Design and Customization: Tailoring Performance
Industrial blower design and customization are critical for maximizing energy efficiency, process reliability, and ROI. Choosing the right configuration ensures compatibility with demanding process conditions—whether handling corrosive fumes, abrasive dust, or extreme temperatures.
Core Design Elements
- Impeller Design: The impeller’s geometry—backward-curved, forward-curved, or radial—directly affects efficiency, pressure, and noise. Backward-curved impellers excel in high-pressure pneumatic systems; forward-curved types are ideal for high-volume ventilation.
- Housing: Heavy-gauge steel or aluminum casings, often treated with anti-corrosive coatings, provide structural strength and environmental resistance.
- Motor Sizing: Electric motors (ranging from 1 to 1,000 HP) are selected to match CFM and pressure requirements, ensuring optimal performance and energy savings.
- Bearings: High-quality roller or ball bearings, designed for extended service life (often 50,000+ hours), withstand high RPMs and harsh operating conditions.
Customization Options
- Material Selection: Stainless steel for food and pharmaceutical processing, fiberglass for chemical resistance, and high-temperature alloys for operations up to 800°F.
- Size and Capacity: Options range from compact 12-inch portable blowers (500 CFM) to massive 10-foot units (50,000 CFM) for power generation and process industries.
- Pressure/Flow Tuning: Tailored impellers, variable frequency drives (VFDs), and custom ductwork achieve precise performance targets.
- Noise Reduction: Acoustic enclosures, silencers, and vibration isolation ensure compliance with workplace noise limits and improve operator comfort.
- Mounting and Integration: Skid-mounted, vertical, or custom-configured units fit into existing plant layouts or tight spaces as needed.
Why Customize?
Customization ensures every blower delivers peak efficiency, safety, and longevity in its unique environment. For example, a blower handling abrasive dust may be fitted with ceramic-coated impellers for extended life, while those in food plants require polished stainless interiors for hygiene. Bespoke designs also minimize energy use and maintenance, cutting total cost of ownership.
Industrial Blower Safety and Compliance Standards
Compliance with industry standards and safety regulations is non-negotiable when specifying or purchasing an industrial blower. In the United States, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) sets the baseline for workplace fan safety, covering guards, electrical safety, and noise. UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification, though not mandatory, demonstrates that a blower meets rigorous safety and performance criteria. Other relevant standards may include AMCA (Air Movement and Control Association) certification for performance ratings, NFPA guidelines for hazardous environments, and international standards such as CE marking for the European market.
Questions about compliance? Consult your blower manufacturer or a qualified safety engineer to ensure your equipment meets all local, national, and industry-specific regulations for your intended application.
How to Choose the Right Industrial Blower
Selecting the best industrial blower for your facility or process is a multi-step process that balances performance, efficiency, reliability, and cost:
- Define Your Application: Clarify the intended use—pneumatic conveying, ventilation, drying, dust collection, or combustion air supply. Each use case dictates specific blower types and configurations.
- Calculate Required Airflow (CFM): Determine the volume of air needed, factoring in room or duct size, process demands, and occupancy. For example, dust collectors for woodworking shops may require 8,000 CFM based on tool output and duct layout.
- Determine Pressure Requirements (in. WG or PSI): Assess total system resistance, including duct length, filters, and equipment. Pneumatic conveying over long distances may require up to 150 in. WG or higher.
- Material & Environment Compatibility: Select construction materials that withstand the operating environment—corrosive fumes (stainless steel/fiberglass), food-grade (316L stainless steel), high temperatures (alloy steel), or explosion-proof requirements (hazardous area rated).
- Motor Sizing and Efficiency: Match horsepower to airflow and pressure needs. Over-sizing increases costs and energy use; under-sizing leads to poor performance and risk of failure.
- Noise and Vibration Control: Evaluate the need for silencers, vibration dampers, or acoustic housing, especially in settings where noise exposure is regulated (e.g., OSHA 85 dB limit).
- Budget, Maintenance, and Lifecycle Costs: Consider not only initial price but also maintenance schedules, part availability, energy efficiency, and projected service life. A costlier, high-efficiency centrifugal blower may offer lower total cost of ownership compared to a budget axial unit.
Request performance data, case studies, or on-site demonstrations from potential vendors. Compare based on CFM, pressure, construction, warranty, and after-sales support. Ensure the selected blower matches your operational demands and offers the best long-term value.
Things to Consider Regarding Blower Manufacturers
With numerous industrial blower manufacturers and suppliers competing for your business, finding the right partner is easier than ever—but making the best choice requires careful consideration:
- Product Range: Does the supplier offer a comprehensive selection of centrifugal, axial, regenerative, and specialty blowers?
- Customization Capabilities: Can they tailor blowers for your specific airflow, pressure, material, and integration needs?
- Certifications & Compliance: Are their products certified to UL, AMCA, OSHA, NFPA, and other relevant standards?
- Technical Support and Service: Do they provide engineering support, installation guidance, maintenance services, and fast access to spare parts?
- Reputation & Experience: Look for companies with proven track records in your industry, strong customer reviews, and robust warranties.
- Value Over Price: While price is important, the lowest-cost option may not provide the reliability, efficiency, or support your operation needs.
Ready to source the ideal industrial blower for your application? Browse our curated list of trusted blower manufacturers and suppliers to request quotes, compare specifications, and find the best fit for your project.
For more information, explore our knowledge base or contact our experts for personalized recommendations on blower selection, sizing, compliance, and maintenance best practices.
Frequently Asked Questions: Industrial Blowers & Fans
- How do I determine my facility’s required CFM and pressure? Use duct sizing calculators, reference process manuals, or consult a ventilation engineer to assess your needs based on room size, ductwork, and equipment.
- What is the difference between a fan and a blower? Fans move high volumes of air at low pressure; blowers deliver air at higher pressures, often for more demanding applications.
- Can industrial blowers improve indoor air quality? Yes—by removing particulates, fumes, and contaminants, they play a critical role in achieving OSHA and EPA air quality standards.
- What maintenance is required for industrial blowers? Typical maintenance includes bearing lubrication or replacement, belt inspection, filter changes, and periodic cleaning of impellers and housings.
- Are high-efficiency blowers worth the investment? Energy-efficient blowers often pay for themselves via reduced utility costs, improved reliability, and lower maintenance expenses over time.
Still have questions? Ask our experts or browse our site for more detailed guides on industrial blower technology, applications, and sourcing strategies.



 Air Compressors
Air Compressors  Air Filters
Air Filters Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Blowers
Blowers Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Industrial Vacuum Cleaning Equipment
Industrial Vacuum Cleaning Equipment Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services